Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has evolved rapidly, and AI agents are at the forefront of this revolution. These intelligent systems can perceive their environment, make decisions, and take actions to achieve specific goals—often without human intervention. From virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa to autonomous business process automation, AI agents are reshaping industries.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore:
-
What AI agents are
-
How they work
-
Different types of AI agents
-
Real-world applications
-
Future trends

What Are AI Agents?
An AI agent is an autonomous system that uses sensors to perceive its environment and actuators to perform actions. Unlike traditional software, AI agents can learn, adapt, and make decisions based on real-time data.
Key Characteristics of AI Agents:
✅ Autonomy – Operate independently without constant human input.
✅ Adaptability – Learn from data and improve over time.
✅ Goal-Oriented – Designed to achieve specific objectives.
✅ Reactive & Proactive – Respond to changes and take initiative.
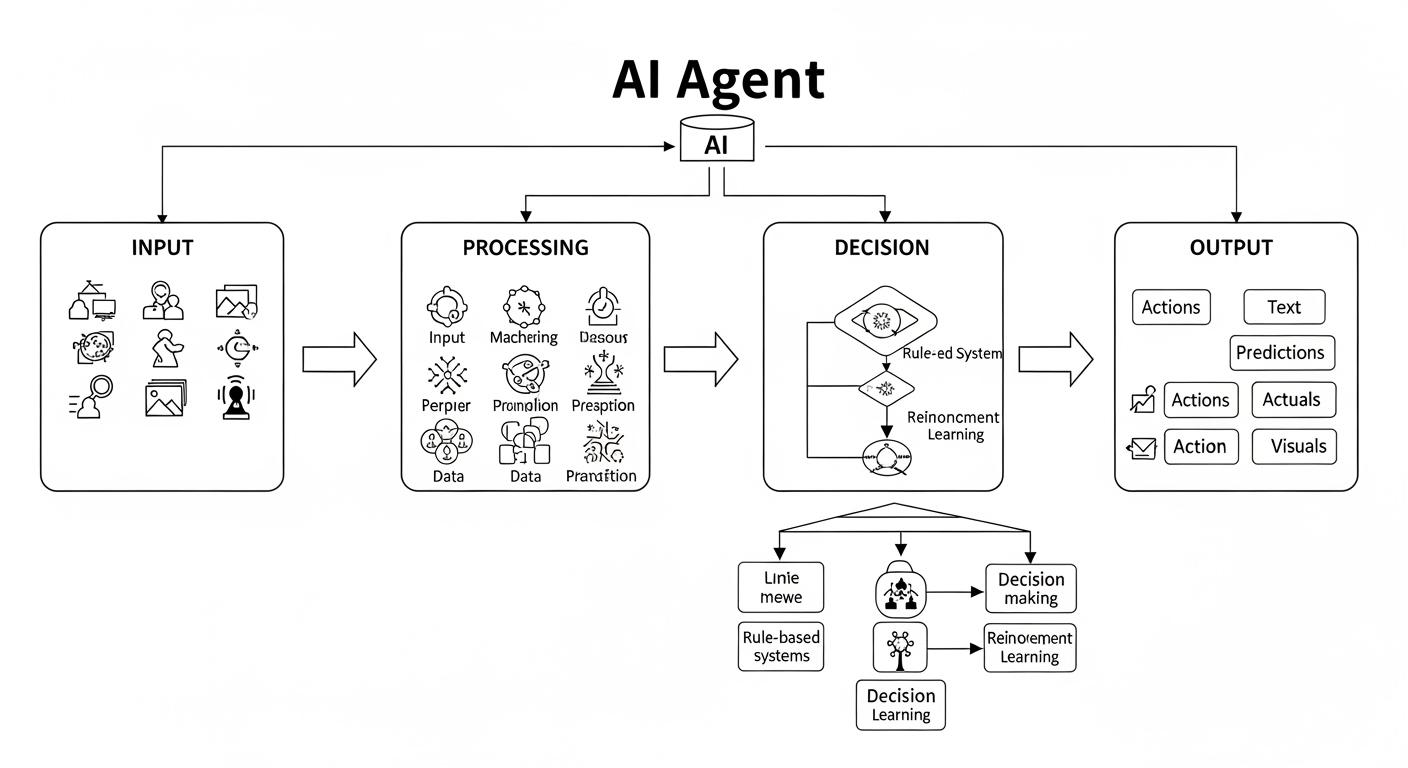
How Do AI Agents Work?
AI agents rely on a combination of technologies:
-
Sensors – Collect data from the environment (e.g., cameras, microphones, APIs).
-
Processing Unit – Uses machine learning (ML) and natural language processing (NLP) to analyze data.
-
Decision-Making – Applies algorithms to determine the best action.
-
Actuators – Execute actions (e.g., sending a response, controlling a robot).
For example, a chatbot (a type of AI agent) processes user messages (input), understands intent via NLP, and generates a response (output).
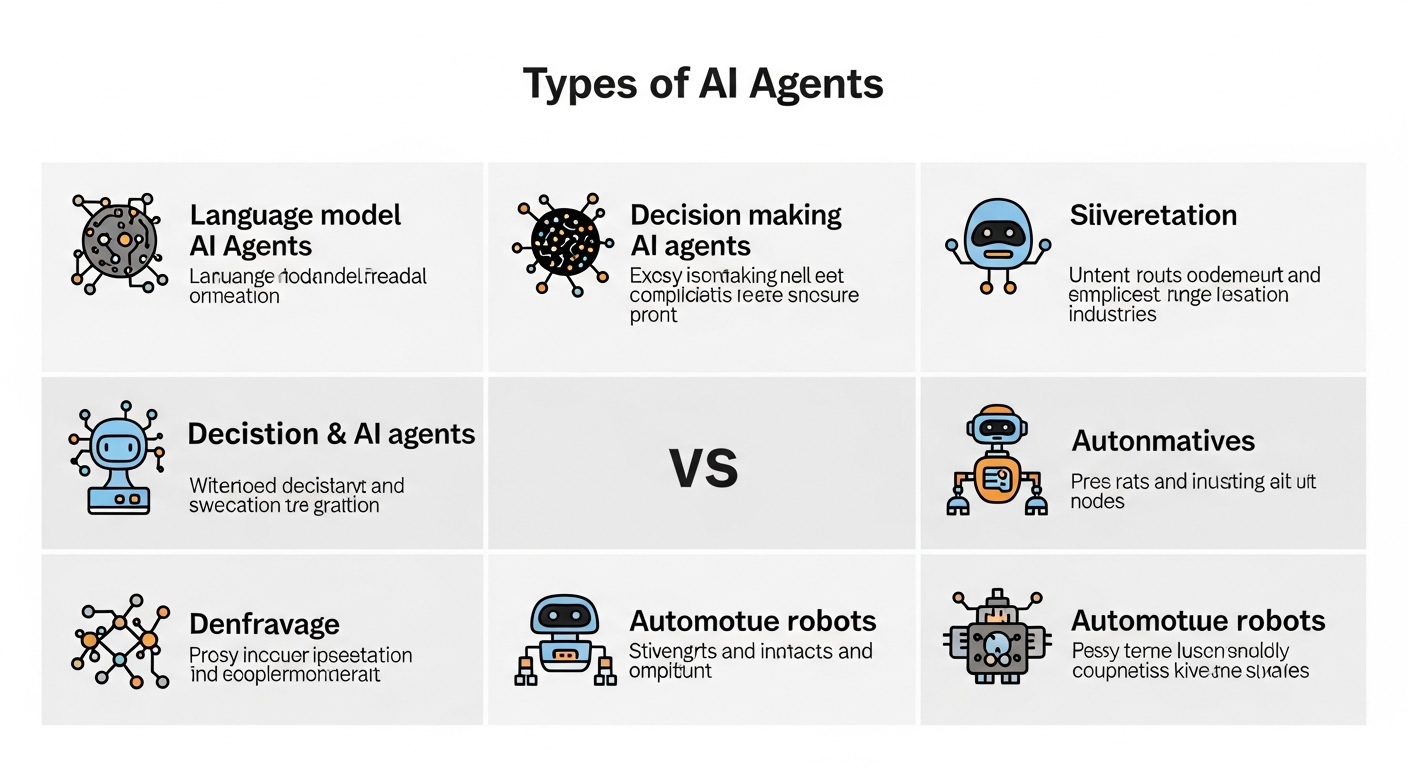
Types of AI Agents
AI agents can be classified based on their complexity and functionality:
1. Simple Reflex Agents
-
React to current inputs based on predefined rules.
-
Example: A thermostat adjusting temperature.
2. Model-Based Reflex Agents
-
Maintain an internal model of the world for better decisions.
-
Example: Self-driving cars predicting traffic patterns.
3. Goal-Based Agents
-
Take actions to achieve specific objectives.
-
Example: AI-powered recommendation engines (Netflix, Amazon).
4. Utility-Based Agents
-
Optimize decisions based on “utility” (best possible outcome).
-
Example: Stock trading bots maximizing profits.
5. Learning Agents
-
Improve performance over time using reinforcement learning.
-
Example: AlphaGo mastering the game of Go.
Real-World Applications of AI Agents
AI agents are already transforming industries:
1. Customer Support (Chatbots & Virtual Assistants)
-
Example: IBM Watson Assistant helps businesses automate customer interactions.
2. Healthcare (Diagnosis & Treatment Planning)
-
AI agents analyze medical data to assist doctors in diagnosis.
3. Finance (Fraud Detection & Trading)
-
Example: AI agents monitor transactions in real-time to detect fraud.
4. Autonomous Vehicles
-
Self-driving cars use AI agents to navigate and avoid collisions.
5. Smart Home Devices
-
Example: Google Nest learns user preferences to optimize energy usage.

Future Trends in AI Agents
The future of AI agents includes:
🔹 Hyper-Personalization – AI agents predicting user needs before they ask.
🔹 Multi-Agent Systems – AI agents collaborating like a human team.
🔹 Emotional AI – Agents detecting and responding to human emotions.
(Image Prompt: A futuristic city where AI agents manage traffic, healthcare, and business operations.)
Conclusion
AI agents are revolutionizing how businesses and individuals interact with technology. From automating customer service to driving cars, their applications are limitless. As AI continues to evolve, these agents will become even more intelligent, adaptive, and integral to our daily lives.
Want to integrate AI agents into your business? Explore Google Cloud’s AI solutions or IBM’s AI agents for enterprise applications.
